Search for
SupportHigh Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Unraveling Causes, Symptoms, and Significance

Inflammation is the body's response while fighting an infection or healing injuries. The ESR test acts as an indicator of inflammation within the body as a high ESR indicates conditions such as autoimmune disorders or infections.
ESR is a non-specific blood test that is widely used as a marker of underlying illness as it is affordable and is a reliable indicator of inflammation. Thus, it is important to understand the causes and symptoms of elevated ESR, as well as the implications of having higher values.
Understanding Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
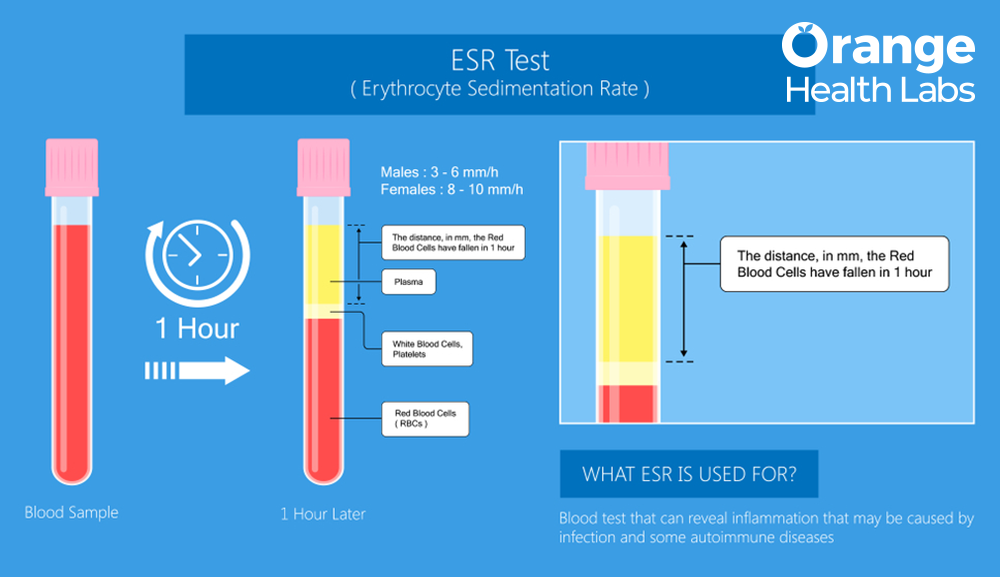
ESR can be defined as the rate at which the red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample settle at the bottom of a test tube. When there's inflammation or cell damage in the body, the cells stick together and settle at a faster rate, thus increasing ESR.
As mentioned above, ESR is a non-specific indicator of inflammation, which means increased ESR levels are not specific to a particular disease. Also, ESR levels may sometimes rise even in the absence of inflammation, since ESR is influenced not only by characteristics of RBC but also by the concentration of albumin protein and immunoglobulins present in the blood. Conversely, certain inflammatory conditions can exist even with a normal ESR level, which makes it a non-definitive diagnostic test.
High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Causes and Significance
If you are wondering what happens if erythrocyte sedimentation rate is high in the body, here is the answer to your question:
- Inflammation: Inflammation involves an increase in the acute-phase proteins that make your RBCs stickier and heavier, decreasing their settling time and increasing ESR levels as seen in various inflammatory conditions.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus involve the overactive immune system destroying the body’s own cells, leading to increased ESR levels.1
- Infections: When harmful microorganisms enter the body, its defence system gets activated. Acute phase proteins known as pentraxins help the body to defend against infections, which ultimately results in increased ESR levels as discussed above.
- Tissue Damage: In case of tissue damage caused by trauma/injury, again acute phase proteins are produced by the liver, resulting in increased ESR levels.
Symptoms Associated With a High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
ESR is a marker of inflammation in the body and is not disease-specific. Therefore, elevated ESR does not cause (lead to) specific symptoms of its own. Rather, it reflects the symptoms of the underlying condition. Some high ESR causes and symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling caused by conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, gout and ankylosing spondylitis
- Fatigue and general malaise as a result of chronic inflammation in the body
High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): What It Indicates?
If you are wondering what does high ESR mean, here’s what you can interpret and use it for:
- Diagnosing disease/conditions: A high ESR indicates the presence of inflammation in the body due to an underlying condition. Further investigations can be done to diagnose the condition.
- Disease monitoring: The ESR level is directly proportional to the amount of inflammation caused by the disease. So, if the disease is improving, the amount of inflammation lessens and ESR levels reduce over time, and vice-versa. Thus, ESR is used to monitor disease progression in inflammatory conditions like temporal arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatic and rheumatoid arthritis. Also, a high ESR may indicate poor outcomes in certain tumours like Hodgkin’s disease.
Reasons for Raised ESR
Some of the reasons for raised ESR can be:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections stimulate the immune response of the body, leading to the release of acute phase proteins, which results in inflammation and, ultimately, increased ESR levels.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In autoimmune conditions, the body’s own immune system damages the tissues, which raises ESR levels.
- Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: In diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, there is excessive immune system response to gut bacteria, which leads to inflammation, thus increasing ESR.
- Cancers: Chronic inflammation is also related to abnormal cell growth causing cancer, and the advancement of cancer can, in turn, trigger the body's acute phase response leading to inflammation, which explains the high ESR levels seen in cancer.
Causes of Elevated ESR
Besides diseases, ESR can be high in some physiologic conditions such as:
- Old age and in women.
- Pregnancy - In pregnancy, plasma proteins like fibrinogen and gamma globulins go up, which leads to a temporary increase in ESR.
- Anaemia causes changes in the RBCs, which in turn may cause high ESR levels.
Interpreting High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Results
Occurrences of both false negatives and false positives are seen when measuring ESR. Also, since high ESR warrants further investigations to diagnose the underlying cause, it is essential to discuss your ESR results with a doctor for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Typically, a CRP test is done alongside ESR for more insight. Other tests, such as imaging tests, may also be needed.
The Significance of Monitoring ESR
- Disease progression: If the underlying disease worsens, ESR levels rise consistently, and conversely, if the inflammation due to the disease decreases, the ESR levels decrease. Thus, ESR levels can be used as an index of disease activity and monitor the progress of certain diseases mentioned before.
- Treatment response: ESR levels also help assess the body’s response to treatment in certain conditions such as osteomyelitis. If ESR falls, this suggests reducing the severity of the inflammation, which in turn may indicate the efficacy of treatment.
To conclude, elevated ESR results offer important insights into underlying health conditions. However, it's essential to understand that a high ESR is an indicator, not a diagnosis, and professional medical advice is necessary. Additional tests may be recommended by your healthcare provider for a precise diagnosis. This is also a great time to consider comprehensive health checkups, such as Tax Saver Health Checkup packages, which include tests like CBC with ESR and Haematology 2 (Hb TC DC & ESR). These packages not only address your immediate testing needs but also provide a cost-effective approach to monitoring your overall health, all with the convenience of doorstep services from Orange Health Labs.
High Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): Unraveling Causes, Symptoms, and Significance

Is Your Child Growing at a Healthy Rate? Key Milestones
